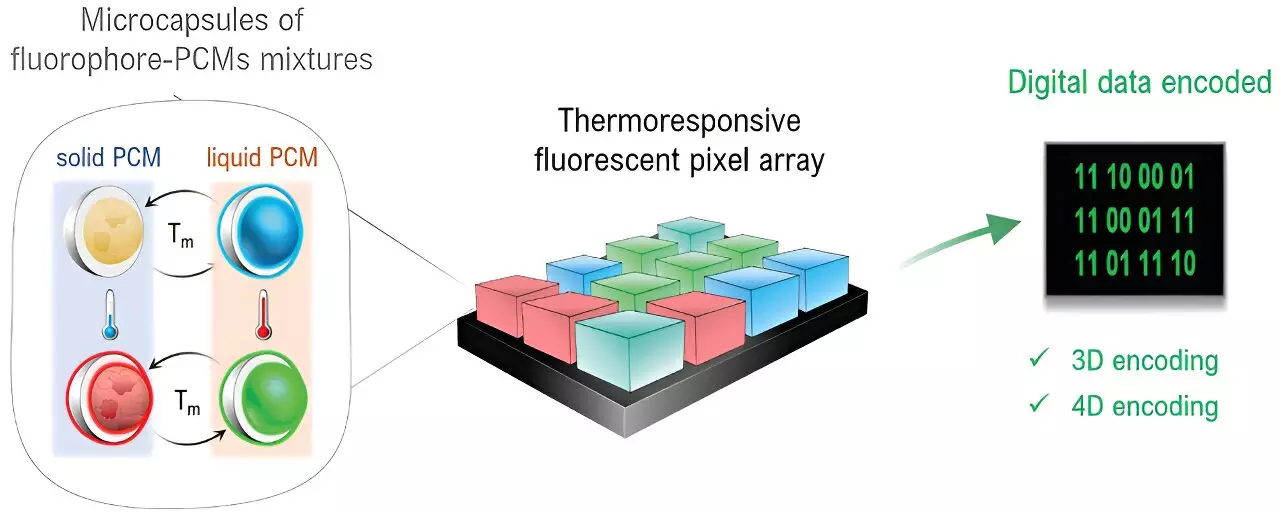
In a groundbreaking development within the realm of digital technology, researchers have unveiled a pioneering data encoding and storage system that leverages microcapsules filled with luminescent dyes and phase change materials (PCMs). This advancement signifies a remarkable leap forward, potentially transforming the landscape of cybersecurity and anti-counterfeiting measures. The research, spearheaded by notable figures like Dr. Claudio Roscini and Prof. Daniel Ruiz-Molina from the ICN2 Nanostructured Functional Materials Group, in collaboration with experts from the Autonomous University of Barcelona (UAB), showcases the synergy between material science and digital security.
At the core of this innovative system is a novel pixel architecture built from microcapsules that contain a unique blend of fluorescent dyes and PCMs, such as paraffins. These materials possess intriguing thermal properties, traditionally recognized for their ability to absorb and release heat based on temperature fluctuations. The researchers ingeniously harnessed these phase transitions to develop a multifaceted data encoding scheme. By encoding data not just through conventional means but also through the color shifts produced by varying temperatures, this research introduces a fresh paradigm in data storage capabilities.
The system operates on two primary principles, facilitating sophisticated encoding operations that can handle both three-dimensional (3D) encryption and four-dimensional (4D) storage. In this context, the three dimensions incorporate spatial positioning, akin to QR codes, along with a spectrum of colors emitted by the microcapsules to enhance the informational depth. The innovative addition of time, as the fourth dimension, allows the system to interpret changes in light emissions based on temperature alterations. Such complexity positions this technology as a formidable contender in high-density data storage solutions that require both security and efficiency.
The potential applications for this technology are vast and varied, bridging the gap between high-efficiency storage and cutting-edge anti-fraud initiatives. In a world increasingly marred by counterfeit goods and digital breaches, the adoption of this digital encoding method could offer a robust mechanism to authenticate products and secure sensitive information. With its cost-effective and user-friendly nature, this technology could democratize advanced data storage solutions, making them accessible to a wider audience and possibly instigating a paradigm shift in how we perceive digital security.
As digital threats evolve, the integration of innovative materials and ingenious encoding techniques is critical. The research conducted by this collaborative team represents not only an impressive scientific endeavor but also a significant step towards a more secure and efficient digital future. By blending practical applications with advanced scientific principles, this technology holds the promise to redefine our approach to data storage and encryption for generations to come. The implications for cyber safety and product authentication underscore a revolutionary initiative that could change the way we protect and store information in a rapidly advancing digital landscape.